- The measure of central tendency are operations that are performed on a set of data to obtain the centre of a dataset i.e. where most of the values lie e.g. In the data set 2,2,4,4,3 it is visible that the centre point of the data is 3 as two values are just less than 3 and two are just more than 3.
- There are various ways to Measure Central Tendency, which we will be looking at in the next sections:
Mean
- Mean is the average of values in a data set for e.g. Total percentage of a student obtained in an exam is the mean of the percentage of individual subjects i.e. Ram got 90% overall implies that average/mean of the percentage of individual subjects of Ram is 90%.
Types of Mean
Arithmetic Mean:
- This is the simplest and most used way of the calculating mean.
- It indicates the central tendency by using sum of the data elements
- This is calculated by adding up all the members of a data set and dividing them by total numbers of elements in the data set.
Example 1:
Dataset: 2,4,5,6. Let us calculate its Arithmetic Mean
- Solution: Sum of all Elements of Dataset = 2+4+5+6 = 17
- Total number of Elements in Dataset = 4
- Hence, Arithmetic Mean = 17/4 = 4.25
Formula
- The Formula to calculate Arithmetic Mean can be written as: Mean =

- where, Xi is the sum of all elements of a data set
- and n is the total number of elements in Set
Example 2:
- Given below is the score obtained by students of a class, calculate the Mean.
| Score
|
Number of Students
|
| 0-2
|
10
|
| 2-4
|
12
|
| 4-6
|
15
|
| 6-8
|
8
|
| 8-10
|
5
|
- Solution:
- To find Mean of a Continuous Dataset, the following steps are being followed:
- Step 1:
- Calculate the mid-point of the distribution (f) and Multiply it with the number of students falling in that range.
| Score
|
Number of Students (x)
|
Mid-Point of Score (f)
|
f*x (Mid Score * No. of Students)
|
| 0-2
|
10
|
1
|
10
|
| 2-4
|
12
|
3
|
36
|
| 4-6
|
15
|
5
|
75
|
| 6-8
|
8
|
7
|
56
|
| 8-10
|
5
|
9
|
45
|
- Mean of a Continuous Distribution = ∑ f*x / (total number of students)
- Mean = (10+36+75+56+45)/50 = 4.44
Geometric Mean
- It is also a method to find Central tendency mean. It uses the product of values of a data set to find the central tendency
- There is just one limitation of this method that it cannot be used on negative numbers.
- In a data set having n elements, Geometric Mean is calculated by taking root of the product of all elements.
Example 3:
Dataset: 2,4,5,6. Let us calculate its Geometric Mean
- Solution: Product of Elements = 2*4*5*6 = 240
- Number of Elements = 4
- Hence, Geometric Mean =
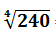 = 3.94
= 3.94
Formula
- The Formula to calculate Geometric Mean can be written as:
- Geometric mean =

- where,
 the product of all the elements xn
the product of all the elements xn
- and n is the total number of elements in the data set.
Harmonic Mean
- It is also a method to calculate the mean that uses the reciprocal of sum of each element of a dataset.
- The harmonic mean is the reciprocal of the arithmetic mean of reciprocals.
Example 4:
Dataset: 2,4,5,6. Let us calculate its Harmonic Mean
- Solution: Reciprocal of all Elements = 1/2, 1/4, 1/5, 1/6
- Sum of Reciprocals = 1/2 + 1/4 + 1/5 +1/6 = 10/9
- Arithmetic Mean of Reciprocals = (10/9)/4 = 10/36
- Reciprocal of Mean of Reciprocals = 36/10 = 3.6
- Hence, Harmonic Mean = 3.6
Formula
- The Formula to calculate Harmonic Mean can be written as:
- Harmonic Mean =

- where xi , is the element of dataset and
- n is the total number of elements in data
Median
- It is the value of the middle element of the data set that has been sorted in ascending or descending order.
- In the case of an odd number of elements in the data set, the middle item is easy to identify e.g. 4th element in a set of 7 elements.
- In case of even number of elements, the middle term is taken to be the average of the two middle terms e.g. average of 4th and 5th element in case of data set of 8 elements.
Example 5:
Dataset A: 2,5,4,6,7 and Dataset B: 2,5,6,4,7,1. Let us calculate the median of both datasets.
- Solution: Sorting Dataset A in Ascending Order: 2,4,5,6,7
- Sorting Dataset B in Descending Order: 7,6,5,4,2,1
- Number of Elements in Dataset A = 5 and Dataset B = 6
- Hence, for A, Median will be the middle term i.e. 3rd Term of sorted dataset = 5 and
- For B, Median will be some of the two middle terms i.e. 3rd term and 4th term of sorted dataset = (5+4)/2 = 4.5
Formula:
Hence, the formula for calculating the Median can be written as:
- If the number of elements n odd
- Median =
 term
term
- If the number of elements n is even
- Median =

Example 6:
- Let us consider a dataset : 3,5,3,4,3,4,5,2,6,7,3,. Let us Calculate its Median.
- Solution:
- Let us sort the data in ascending order: 2,3,3,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,7
- Creating a frequency distribution of the above data,
| Number
|
Frequency
|
| 2
|
1
|
| 3
|
4
|
| 4
|
2
|
| 5
|
2
|
| 6
|
1
|
| 7
|
1
|
- Total Frequency = Number of Elements= 11
- As the number of terms is 11, the Median will be the middle term i.e 6th term.
- Hence, Median = 4
- Note: The Median can either be obtained by counting the 6th element in the dataset or if the dataset is given as frequency distribution, then add up the frequency until we get the required frequency 6, which is for number 4 in this case, hence the median will be 4.
Mode
- The mode of a data set is the element that has the highest frequency in the entire data set i.e. the highest number of occurrences. A dataset can have one or mode modes.
- Data set with two modes is bimodal, three modes are trimodal and more than three modes is multimodal.
Example 7
| Dataset
|
Dataset Elements
|
Mode
|
Type
|
| A
|
2
|
5
|
5
|
2
|
6
|
7
|
2
|
2
|
Unimodal
|
| B
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
5
|
6
|
4
|
3
|
5,6
|
Bimodal
|
| C
|
2
|
5
|
6
|
2
|
5
|
6
|
4
|
2,5,6
|
Trimodal
|
- Mode for a Continuous Dataset can be calculated by using the following Formula:
- Mode = L +
 * R
* R
- Where L is the Lower limit of the Range,
- R is the size of the Range
- D1 is the highest frequency
- D0 is the frequency preceding D1
- D2 is the frequency succeeding D1
- Let us take the following example to clarify the above formula,
Example 8:
- Given below is a survey data of a society regarding number of vehicles in a family:
| No. of Vehicles
|
0-2
|
2-4
|
4-6
|
6-8
|
8-10
|
| Number of Families
|
6
|
10
|
5
|
2
|
1
|
- Mode = L +
 * R
* R
- Step 1: Highest frequency = 10, its corresponding range = 2-4
- Step 2: L = 2; R = 4 – 2 = 2; D1 = 10, D0 = 6, D2 = 5
- Step 3: Mode = L +
 * R
* R
- Mode = 2 +
 * 2 = 2 + 0.89 = 2.89
* 2 = 2 + 0.89 = 2.89
= 3.94
the product of all the elements xn
term
* R
* R
* R
* 2 = 2 + 0.89 = 2.89






